
CONDITIONS TREATED
Dr Declan Sweeney provides specialised orthotic assessment and treatment for common foot and lower-limb conditions. Each treatment is based on a detailed clinical evaluation and gait analysis, with orthotic solutions tailored to the individual to relieve pain, improve function, and support long-term mobility.
Plantar Fasciitus
Plantar fasciitis is a common cause of heel pain, often felt as sharp or stabbing discomfort beneath the heel, particularly during the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of activity.
Treatment focuses on identifying abnormal foot mechanics that place excessive strain on the plantar fascia. Custom orthotic support is prescribed to improve alignment, redistribute pressure, and reduce stress on the heel, allowing inflammation to settle and function to improve.

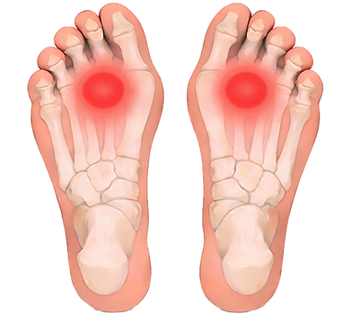
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia refers to pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot, frequently described as burning, aching, or sharp discomfort during walking or standing.
Orthotic treatment is designed to off-load excessive pressure from the forefoot by improving weight distribution across the foot. This helps reduce pain, improve comfort, and allow a return to normal daily activities.
Excessive Pronation
Excessive pronation occurs when the foot rolls inward excessively during walking or running. Over time, this can contribute to pain in the feet, ankles, knees, and lower legs.
Assessment focuses on gait mechanics and lower-limb alignment. Custom orthoses are designed to provide appropriate support and control, promoting a more efficient and stable walking pattern.


Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a painful condition caused by irritation or compression of a nerve in the forefoot, most commonly between the third and fourth toes. Symptoms often include burning pain, tingling, or the sensation of standing on a small object.
Orthotic management aims to reduce pressure on the affected nerve by improving forefoot alignment and redistributing load. This approach can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent progression.
Tibialis Posterior Tendinitis
The tibialis posterior tendon plays an important role in supporting the arch of the foot. Dysfunction of this tendon can lead to pain along the inside of the ankle and foot, along with progressive flattening of the arch.
Treatment involves addressing abnormal foot mechanics that place excessive strain on the tendon. Custom orthotic support is used to improve arch support, enhance stability, and reduce stress on the tendon during movement.


Shin Splints (Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome)
Shin splints are a common overuse injury that causes pain along the front or inner edge of the shin bone (tibia). They are frequently experienced by runners, walkers, and athletes involved in repetitive impact activities. The discomfort often begins as a dull ache and can progress to sharper pain during or after exercise if left untreated.
Shin splints typically develop when the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue around the shin become overloaded. Contributing factors include sudden increases in activity, poor footwear, running on hard or uneven surfaces, and biomechanical issues such as excessive foot pronation.
Early treatment is important to prevent symptoms from worsening. Management commonly includes activity modification, rest, ice, and a gradual return to exercise. Addressing underlying biomechanical causes is key to long-term relief.
Runner’s Knee (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome)
Runner’s knee is a common condition that causes pain around or behind the kneecap (patella). It often affects runners, walkers, and people involved in activities that place repetitive stress on the knee. Symptoms typically include a dull ache at the front of the knee, which may worsen during running, stair climbing, squatting, or after sitting for long periods.
Runner’s knee usually develops when the kneecap does not track smoothly over the thigh bone. This can be influenced by muscle imbalances, training errors, poor footwear, or biomechanical issues in the feet and lower limbs. Excessive foot pronation, in particular, can increase stress through the knee by altering leg alignment during movement.
Treatment focuses on reducing pain, improving movement, and addressing contributing factors. This may include activity modification, strengthening and stretching exercises, and improving footwear.







